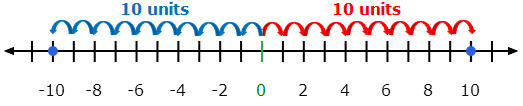
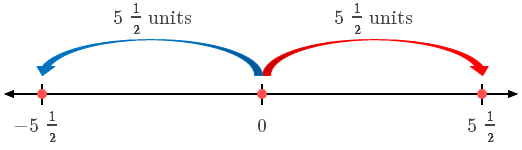
Positive & Negative Numbers
6th Grade
|
|
|
Alabama Course of Study Standards:
9
|
Use signed numbers to describe quantities that have opposite directions or values and to represent quantities in real-world contexts. |
Arizona Academic Standards:
6.NS.C.5
|
Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values. Use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world context, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. |
Common Core State Standards:
Math.6.NS.5 or 6.NS.C.5
|
Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together
to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g.,
temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level,
credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and
negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts,
explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. |
Georgia Math and ELA Standards:
6.NR.3.1
|
Identify and compare integers and explain the meaning of zero based on multiple authentic situations. |
North Carolina - Standard Course of Study:
6.NS.5
|
Understand and use rational numbers to:- Describe quantities having opposite directions or values.
- Represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation.
- Understand the absolute value of a rational number as its distance from 0 on the number line to:
- Interpret absolute value as magnitude for a positive or negative quantity in a real-world context.
- Distinguish comparisons of absolute value from statements about order.
|
New York State Next Generation Learning Standards:
6.NS.5
|
Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values. Use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation.
e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, debits/credits, positive/negative electric charge |
Tennessee Academic Standards:
6.NS.C.5
|
Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. |
Alabama Course of Study Standards:
10.a
|
Define opposites as numbers located on opposite sides of 0 and the same distance from 0 on a number line. |
Arizona Academic Standards:
6.NS.C.6a
|
Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself and that 0 is its own opposite. |
Common Core State Standards:
Math.6.NS.6a or 6.NS.C.6.A
Kentucky Academic Standards (KAS):
6.NS.6.a
Mississippi College- and Career-Readiness Standards:
6.NS.6a
|
Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations
on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the
opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself, e.g.,
–(–3) = 3, and that 0 is its own opposite. |
Georgia Math and ELA Standards:
6.NR.3.2
|
Order and plot integers on a number line and use distance from zero to discover the connection between integers and their opposites. |
North Carolina - Standard Course of Study:
6.NS.6.a
|
On a number line:- Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 and that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself.
- Find and position rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line.
|
New York State Next Generation Learning Standards:
6.NS.6.a
|
Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line. Recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself, and that 0 is its own opposite.
e.g., With the number 3, – (–3) = 3. |
Tennessee Academic Standards:
6.NS.C.6.a
|
Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself. For example, - (-3) = 3, and that 0 is its
own opposite. |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
CC.2.1.6.E.4
|
Apply and extend previous understandings of numbers to thesystem of rational numbers. |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
M06.A-N.3.1.1
|
Represent quantities in real-world contexts using positive and negative numbers, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge). |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
M06.A-N.3.1.2
|
Determine the opposite of a number and recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself (e.g., –(–3) = 3; 0 is its own opposite). |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
M06.A-N.3.1.3
|
Locate and plot integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line; locate and plot pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane. |
Georgia Math and ELA Standards:
6.NR.3.1
|
Identify and compare
integers and explain the
meaning of zero based on
multiple authentic
situations. |
Arkansas Academic Standards:
6.NCC.1
|
Explain positive and negative integers as being opposite values or directions and the meaning of 0 in a real-world context. |
|
|


 6th Grade Math - Positive & Negative Numbers Lesson
6th Grade Math - Positive & Negative Numbers Lesson